Security Concerns on Global Maritime Industry
When concerns arise for maritime security.
In 2021, the Evergreen ship’s blockage of the Suez Canal significantly affected maritime industry. Fast forward to two years, to a different socio-political landscape, and new concerns arise about a potential blockage in the Bab al Mandeb Strait impacting oil and fuel prices. Yemen’s Houthi rebels, engaged in regional conflict linked to Gaza, have attacked vessels in retaliation against Israel. Major shipping companies temporarily ceased operations in this vital area. In response, the US announced the formation of the “Guardian of Prosperity” coalition to protect vessels in these waters.
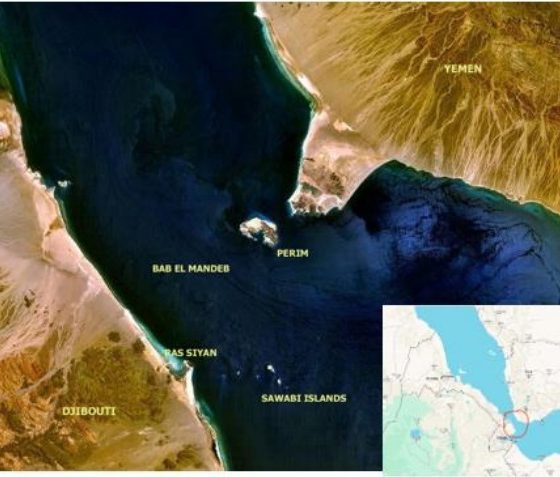
Where is the Bad al Mandeb Strait?
The Bad al Mandeb Strait, which lies between the coasts of Eritrea and Djibouti to the west and the coast of Yemen to the east, connects the Indian Ocean to the Red Sea, which connects to the Mediterranean through the Suez Canal. The sea route through Suez and Mandeb is the shortest of those linking Asia and Europe by sea. therefore the Houthi-threatened strait is a key international trade enclave. Most oil and gas exports from the Persian Gulf follow this route. A blockade could force European ships to go around Africa or navigate the Arctic Ocean, leading to increasing fuel prices. Qs evidenced by a 1% oil price spike following British Petroleum’s supply route adjustments announcement.
Why are they attacking this strait and impact on maritim industry?
The Houthis, a political-religious group – similar to Hezbollah, are a Yemeni Zaidi Shiite group engaged in a longstanding conflict against Yemen’s government and Saudi Arabia. Controlling the northwest, including the capital Sana’a and the Red Sea coastline. The Houthis uprose in 2004 to overthrow President Saleh, later becoming entangled in the Arab Spring and the subsequent civil war. The conflict, involving a coalition led by Saudi Arabia and the UAE, has resulted in nearly 377,000 deaths and a humanitarian crisis affecting 14 million Yemenis.
The Houthis do not form a compact political bloc, and there are constant disagreements between their military and religious leaders. It is known that the group receives funds and weapons from Hezbollah and Iran, which are part of the so-called “Axis of Shia Resistance”, a politico-religious alliance opposed to the United States, Israel and Salafist countries such as Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. The fighting against these two Arab countries has been ongoing since 2015. Although, this year, important negotiations were taking place between the Saudis and the Houthis to end the conflict. The Houthis, which oppose Israeli’s intervention, have attacked ships and will continue to launch rocket despite U.S. statements.
Consequences for the Maritime Industry
The consequences of the conflict extend beyond the immediate region. Suez Canal traffic declined by 35%, impacting Asian trade and causing delayed responses. Forcing ships to go through Africa’s Cape of Good Hope instead of the Suez Canal. This new route increases travel time from seven to 30 days, resulting in slower trade and higher prices for goods.
Black Bull Group, part of ES-KO group offer consultancy services in complex, high-risk and emerging markets. Providing protection, prevention and risk mitigation plans when and where they are needed most.


